Git Projects
This guide covers integrating xltrail with external Git repositories.
If you prefer to learn about setting up a drag-and-drop project, refer to the Drag-and-Drop Projects.
In xltrail-speak, a Git project is a Git repository, owned by you, and hosted on a service like GitHub, Gitlab, Bitbucket or Gitea.
When you set up a Git project in xltrail, you provide xltrail with the url and access token to your repository. xltrail then creates a mirror clone of your repository and keeps it in-sync as you work on your repository.
Create a Git Project via HTTP(S)
On the landing page, click on the + New Project button:
This will open a dialog from where you can select Git Integration and provide the URL, username and token. If possible, generate a read-only token instead of using your regular password. Follow the instructions below for the most popular Git providers.
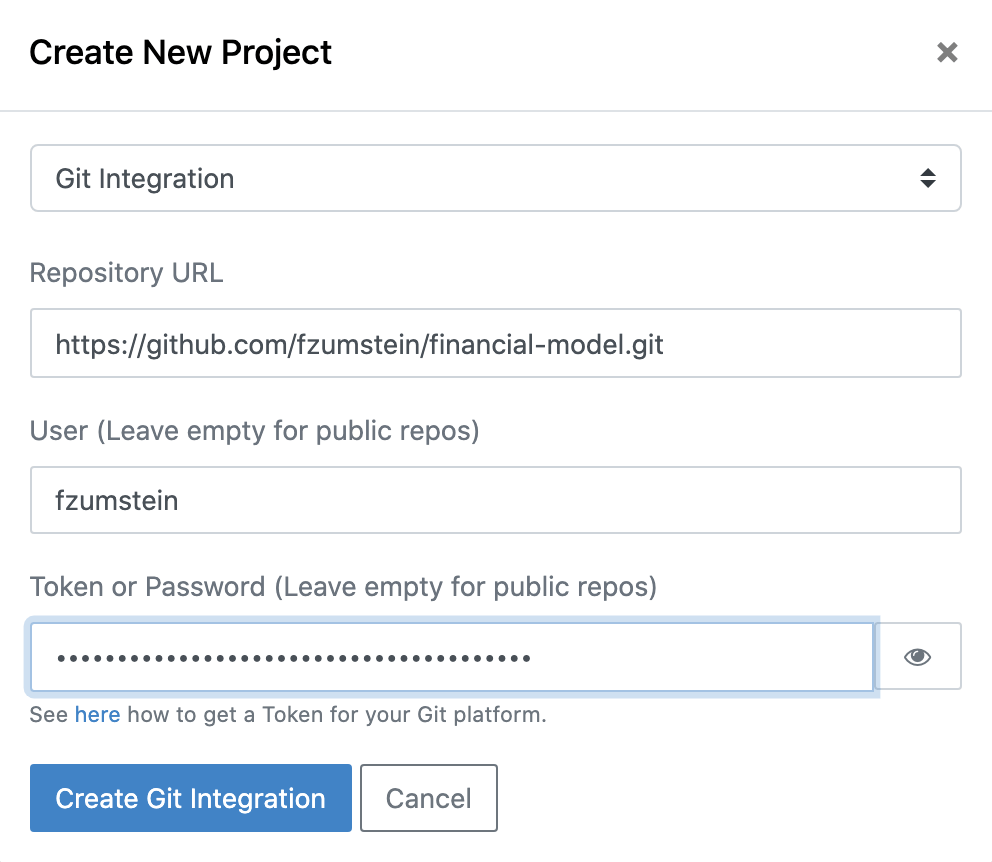
Make sure to paste the HTTP(S) (and not the SSH) version of your Git URL. Also, if your Git provider (e.g. Bitbucket) starts the URL with your username, make sure to remove it including the @. While this should be done automatically by xltrail, it's good to double-check in case your credentials are not accepted.
Depending on the size of your Git repo, the initial syncing may take anything from a few minutes to a few hours: You will be able to check the progress by clicking the History button in the commit box on the Workbook View.
How to Generate Tokens
Depending on the Git provider you use, the tokens may give you access to a single repository or all repositories that your user can access.
Github Cloud & Enterprise
Under Personal settings > Developer settings > Personal access tokens, you can Generate new token. Tick the
repo checkbox so you get access to all the subitems in that box.
If your company is using a Single Sign On (SSO) service like e.g. Okta, you'll need to make sure to enable your token for SAML, see: https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/authorizing-a-personal-access-token-for-use-with-saml-single-sign-on
GitLab Cloud & CE/EE
You can either use a token that is bound to a specific repository or to your user:
Repository Deploy Token
- This requires at least GitLab 10.7
- The token will give you read-only access to a single repository.
- In your repository, go to
Settings>Repository, thenDeploy Tokens(notDeploy Keys!). Give it aName, checkread_repositoryunderScopesand click onCreate deploy token. It will give you both an automatically generatedusernameandtokenthat you'll need to use with xltrail.
Personal Access Token
- You will be able to access every repository that you have access to with a personal access token:
- Create a personal access token under
User Settings>Access Tokens. Tick theread_repositorycheckbox underScopes. Use your GitLab username with that token as password in xltrail. If you are on an older version of GitLab, you might not haveread_repositoryavailable. In that case use theapicheckbox.
Bitbucket Cloud
Personal Accounts: You can create an app password under
Bitbucket Settings>Access Management>App password. Tick the checkboxesRepository (read)andPull Requests (read).Team Accounts: You can create an API key to use with your team name under
Bitbucket Settings>Access Management>API key.
Bitbucket Server
Bitbucket Server (the on-premise version of Bitbucket) introduced personal access tokens with version 5.5, see Bitbucket Cloud above for the details.
On lower versions, you can either use an existing user or create a dedicated xltrail user:
- Log in as Bitbucket administrator
- Under "Administration" click on
Users, thenCreate user - Pick something like
xltrailas the username
To finalize, you need to give this user read access either on Project or Repository level.